Glycochemistry Research Lab
Department of Chemistry
Indian Institute of Technology Bombay
Powai, Mumbai 400076
Phone : 022-2576 7166
Fax : 022 -2576 7152
Email : suvarn[at]chem.iitb.ac.in
Synthesis of trehalose based glycolipids and oligosaccharides :
Several trehalose containing glycolipids and lipooligosaccharides are found in mycobacteria, while a few are isolated from fungi and worms. These glycoconjugates play significant biological roles in survival of these organisms and display immunological properties. They offer avenues for development of target specific drugs and vaccines. These glycoconjugates are present in micro-heterogeneous form in nature and cannot be obtained in ample amount and with desired purity for biological studies. Their highly amphiphilic character and structural diversity arising through, their large number of functional groups (esters, double bonds, COOH, SO4 etc.), additional chiral centres of the side chains, and the point of attachments to the trehalose core makes them challenging synthetic targets. Recently, we completed the first synthesis of a maradolipid isolated from C. elegans, employing mono-acylation of hexaTMS trehalose 6,6′-diol as key desymmetrization step. The methodology was used for the synthesis of symmetric and unsymmetrical analogs of maradolipids.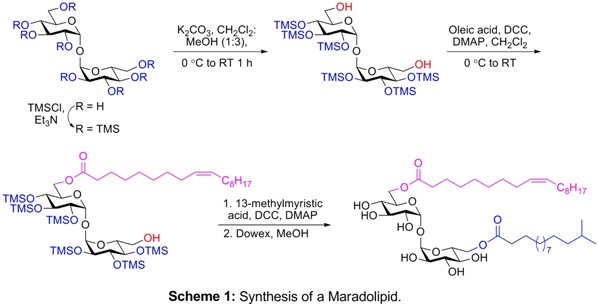 Desymmetrization of trehalose is a long standing problem. A general methodology of desymmetrization of trehalose
is essential for the synthesis of un-symmetrically substituted trehalose derivatives. Regioselective reductive
opening of one of the benzylidene acetals constitutes a short route for desymmetrization of trehalose. We
carried out a systematic study to establish conditions for selective ring opening of only one of the
4,6-O-benzylidene groups of the trehalose dibenzylidene acetals and substituted benzylidene acetals at O6 or O4,
by using DIBAL solution in toluene or in CH2Cl2, respectively to get access to un-symmetrically substituted
6-OH and 4-OH trehalose derivatives. The method was applied to synthesize various biologically important
trehalose glycoconjugates substituted at O4 and O6, including a mycobacterial trisaccharide, a 4-epi
trehalosamine analog and a maradolipid.
Desymmetrization of trehalose is a long standing problem. A general methodology of desymmetrization of trehalose
is essential for the synthesis of un-symmetrically substituted trehalose derivatives. Regioselective reductive
opening of one of the benzylidene acetals constitutes a short route for desymmetrization of trehalose. We
carried out a systematic study to establish conditions for selective ring opening of only one of the
4,6-O-benzylidene groups of the trehalose dibenzylidene acetals and substituted benzylidene acetals at O6 or O4,
by using DIBAL solution in toluene or in CH2Cl2, respectively to get access to un-symmetrically substituted
6-OH and 4-OH trehalose derivatives. The method was applied to synthesize various biologically important
trehalose glycoconjugates substituted at O4 and O6, including a mycobacterial trisaccharide, a 4-epi
trehalosamine analog and a maradolipid. 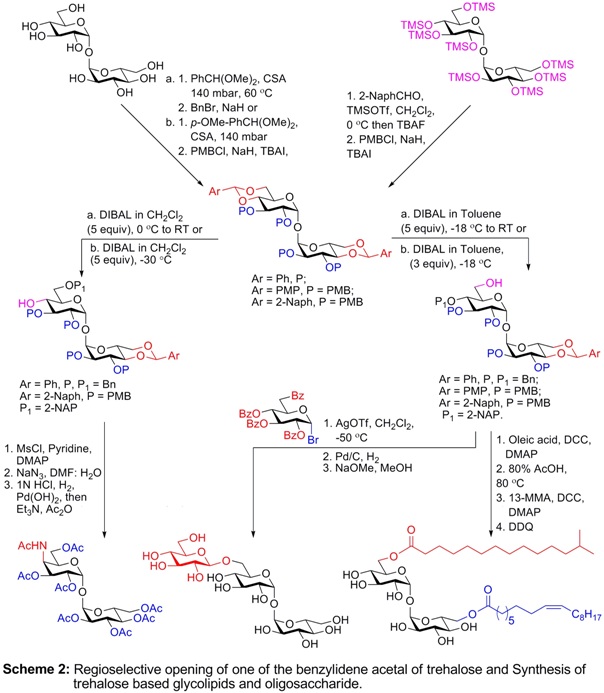
Publications :
- Chaube, M. A.; Sarpe, V.A.; Jana, S.; Kulkarni, S. S. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 5595-5598. DOI :
- Sarpe, V.A.; Jana, S.; Kulkarni, S. S., Org. Lett. , 2016, 18, 76-79. DOI :
- Chaube, M. A.; Kulkarni, S. S. Chem. Eur. J., 2015, 21, 13544-13548. DOI :
- Sarpe, V.A.; Kulkarni, S. S., Org. Lett. 16, 5732-5735, DOI :